ESG reporting (Environmental, Social, and Governance) is the process of collecting, analyzing, and disclosing information about the environmental, social, and governance aspects of an organization’s operations. ESG reporting focuses on three key areas:
- Environmental Aspect: This includes information about the organization’s impact on the environment, such as greenhouse gas emissions, waste management, energy efficiency, and natural resource conservation. The goal is to identify and report on the environmental risks and opportunities the organization faces and how it sustainably manages these issues.
- Social Aspect: This aspect encompasses issues related to the organization’s relationships with its employees, the communities in which it operates, suppliers, and society at large. Examples of social issues include human rights, working conditions, diversity and inclusion, product and service safety, and contributions to the local community.
- Governance Aspect: This refers to how the organization is managed and controlled. It includes information about governance structure, business ethics, corporate responsibility, transparency, risks, and rewards. This aspect also encompasses reporting on ethical principles and policies, as well as corporate risk management.
ESG reporting aims to provide stakeholders with a comprehensive view of an organization’s sustainability and social responsibility, as well as its financial performance. Reporting can be done through various channels, including annual reports, dedicated reports, websites, and other communication tools. ESG reporting is becoming increasingly important as investors, consumers, and regulatory bodies seek more information about the sustainability and social responsibility of the organizations they invest in or collaborate with.
What is the purpose of ESG reporting?
The purpose of ESG reporting is to provide transparent and relevant information about the environmental, social, and governance aspects of an organization’s operations to assess its sustainability and social responsibility. Here are some key objectives of ESG reporting:
- Enhancing transparency: ESG reporting provides relevant information about an organization’s sustainability, enabling stakeholders to better understand its performance and impact on the environment, society, and governance. Transparency helps build trust and allows stakeholders to make informed decisions about engaging in the organization’s business activities.
- Increasing sustainability: ESG reporting encourages organizations to focus on sustainability and social responsibility as integral parts of their operations. Identifying and reporting on environmental and social risks, opportunities, and performance motivates organizations to integrate sustainable practices into their business strategies and operations.
- Improving corporate responsibility: ESG reporting promotes corporate responsibility and reflects an organization’s approach to ethical principles, human rights, transparency, and responsible governance. Reporting on ESG factors helps organizations identify and address weaknesses and improve their policies and practices.
- Creating value for stakeholders: ESG reporting enables organizations to communicate their ESG performance and results to stakeholders, including investors, employees, clients, suppliers, and communities. Through transparent reporting, organizations can enhance their reputation, attract investors, reduce risk, and create long-term value for all stakeholders.
- Comparability and compliance: ESG reporting promotes the development and adoption of international standards and guidelines, such as GRI, SASB, and others. This enables comparability of reports between organizations and facilitates compliance with regulatory requirements and stakeholder expectations.
Ultimately, the goal of ESG reporting is to promote sustainable business, social responsibility, and long-term value creation for organizations and their stakeholders.
Who is required to conduct ESG reporting?
The obligation to conduct ESG reporting can vary depending on the legislation and regulatory requirements of each country or jurisdiction. However, there are some groups of organizations that often have a requirement or pressure to conduct ESG reporting. Here are a few examples:
- Publicly listed companies: Publicly listed companies often have an obligation to report on the ESG aspects of their operations. This may be mandated by legislation, stock exchange regulations, or regulatory bodies. These requirements may apply to companies listed
- Financial Institutions: Financial institutions such as banks, insurance companies, pension funds, and investment funds are increasingly under pressure to report on the ESG aspects of their investment portfolios. This is often a result of investor demands for more information on the ESG performance of the companies they invest in.
- Large Corporations: Large corporations, especially those with a global presence or operating in sectors that have a significant impact on the environment, society, or governance, often engage in ESG reporting. This can be driven by regulatory requirements as well as pressure from stakeholders, consumers, suppliers, and other interested parties.
- Government Organizations: Government organizations, including governments and local authorities, can also engage in ESG reporting to inform the public about their sustainable practices, policies, and results.
It is important to note that there is a growing trend towards expanding the obligation of ESG reporting to a wider range of organizations, including medium-sized enterprises. Additionally, some organizations voluntarily engage in reporting to enhance transparency, accountability, and reputation.
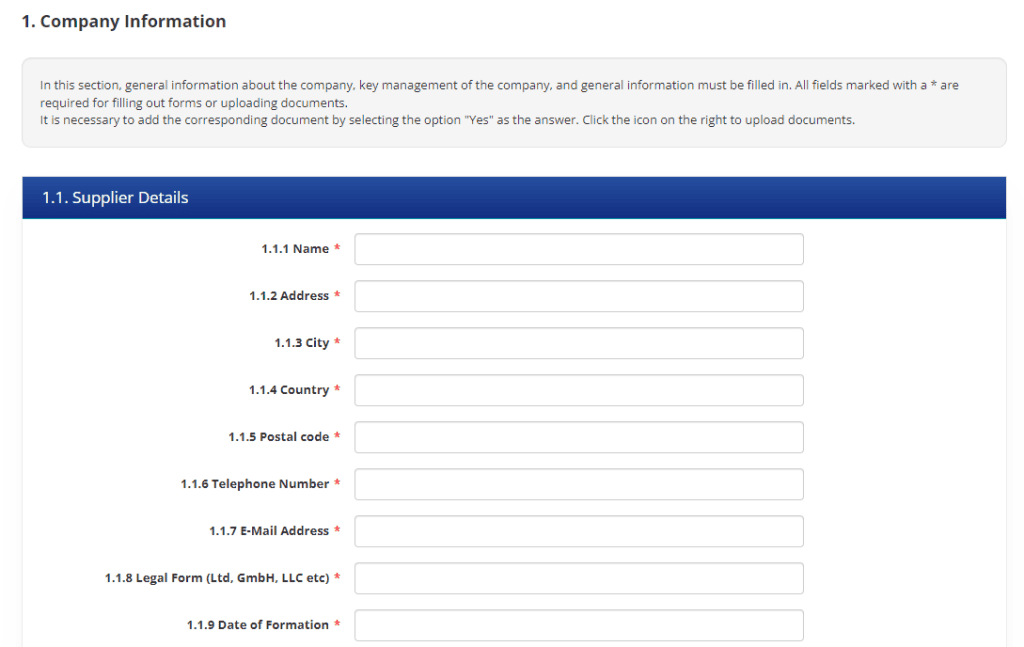
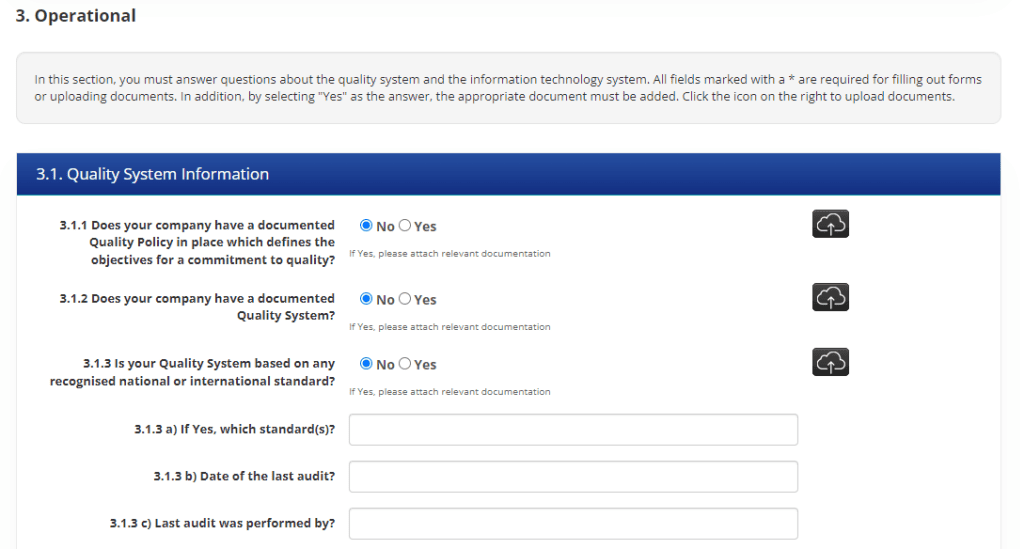
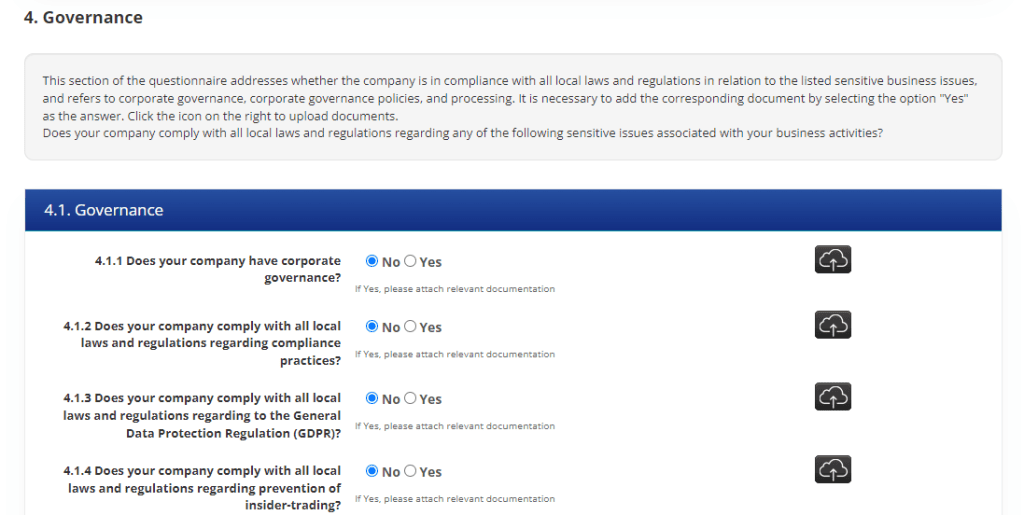
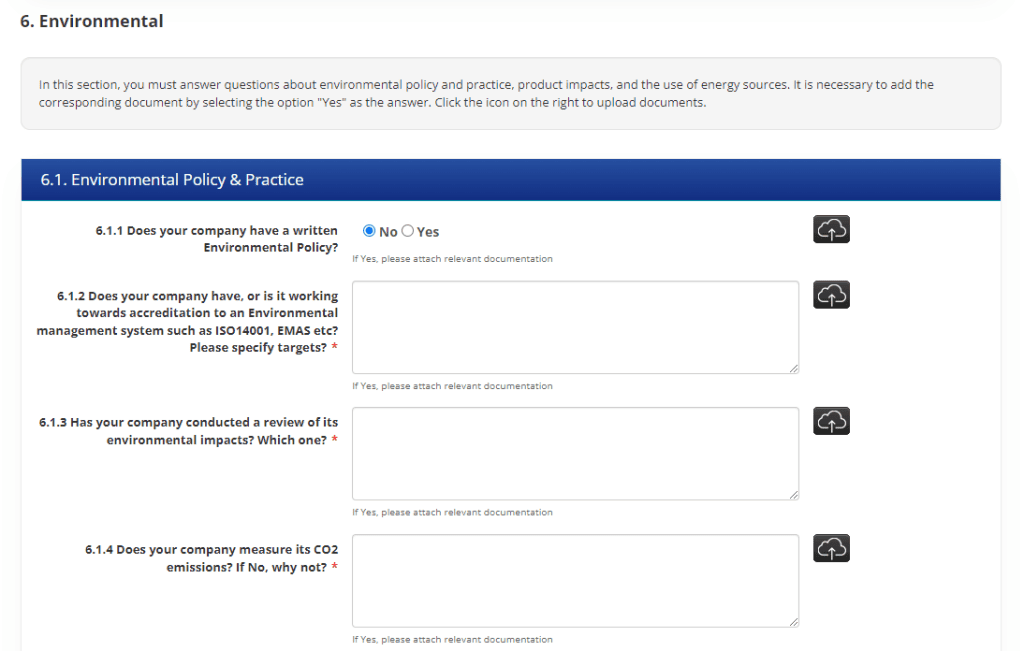
Implementation of Supplier Audit Questionnaire for ESG Reporting Purposes
Ensolva supports the functionality of Supplier Audit Questionnaire (SAQ), which enables customers to conduct comprehensive assessments and verifications of their suppliers digitally. With Ensolva’s customizable SAQ feature, customers can tailor the questionnaire to their specific needs and requirements, ensuring a comprehensive evaluation of suppliers’ sustainable practices.
The SAQ functionality enables the digital collection of key information from suppliers regarding their environmental, social, and governance performance. Ensolva enables customers to assess suppliers’ commitment to sustainability, identify potential risks, and make informed decisions when selecting partners. Transparent and meaningful reporting allows companies to demonstrate their dedication to sustainable development and contribute to building a more resilient and prosperous future for all.